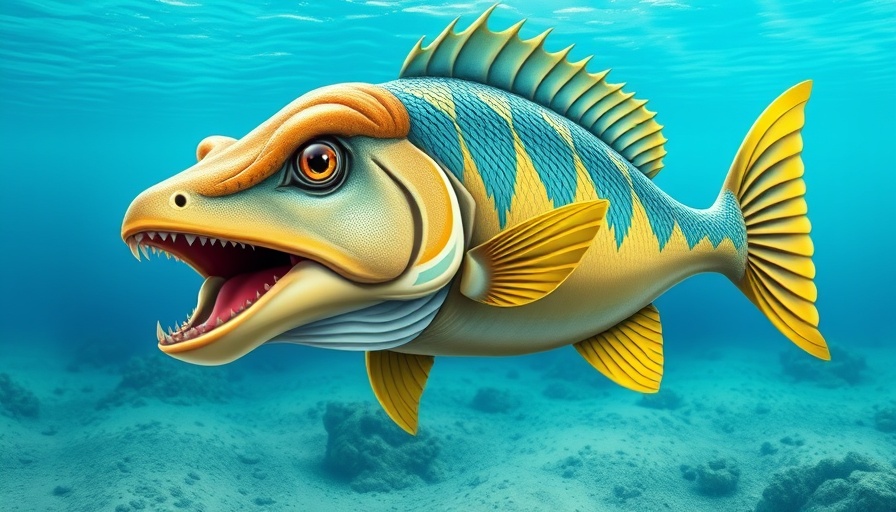

The Hidden Wonders of Evolution: Discovering Platysomus parvulus
A remarkable discovery has illuminated the past of ancient aquatic life, unveiling a 310-million-year-old fossilized fish known as Platysomus parvulus. This remarkable find offers insight into the evolution of feeding mechanisms in fish species, showcasing an adaptation that was previously thought to have emerged much later in the evolutionary timeline. The uniqueness of this fish lies not just in its age but in its sophisticated feeding strategy, which features a 'tongue bite' mechanism.
What is a 'Tongue Bite'?
The 'tongue bite' mechanism consists of specialized teeth located on both the roof and floor of the fish’s mouth—functioning almost like a second jaw. This extraordinary arrangement allows Platysomus parvulus to crush and chew tough food, such as shells and insects, making it versatile in its diet.
Interestingly, while modern fish often rely solely on their jaws for feeding, some species have adopted this innovative approach. It showcases nature's ingenuity in adapting to environmental changes and dietary needs.
A Window into the Past: The Role of Fossils in Understanding Evolution
The aquatic world has long been shaped by mass extinction events, which spur rapid evolution and innovation in surviving species. The recent finding in Staffordshire, England, where the fossil was discovered, not only sheds light on this particular fish species but also serves as a cornerstone for understanding evolutionary biology. Lead author Professor Sam Giles highlights how this discovery helps clarify how fish evolved after the End-Devonian Mass Extinction, which devastatingly reduced biodiversity.
Technological Advances in Paleontology
This groundbreaking study utilized high-resolution CT scanning technology, allowing researchers to digitally dissect the internal anatomy of the fossil. Such advanced techniques are revolutionizing paleontological studies by providing unprecedented insights into species that lived millions of years ago.
Using this technology, researchers uncovered details about Platysomus parvulus that suggest a transitional link between simple jawed fish and more advanced 'tongue-biters' that evolved later, like those in the Bobasatrania group.
Implications for Modern Fish Species
The discovery of this ancient fish underscores a significant truth about evolution: the adaptability of life forms in response to environmental challenges. Modern species with 'tongue bites'—such as trout—demonstrate that this feeding mechanism is still relevant and beneficial in diverse ecosystems.
Understanding such evolutionary traits can help fish conservationists devise better strategies to protect aquatic biodiversity, especially as environmental changes continue to threaten marine habitats.
The Fascination of Fossils:
Fossils like Platysomus parvulus, allow us to connect with Earth's distant past. They reveal stories of adaptation, survival, and the unrelenting march of evolution that continues even today. Such discoveries fuel our curiosity and understanding of life in all its forms, showing just how complex and interconnected our planet's biological history is.
Why This Matters to You:
For individuals interested in the evolutionary sciences, these findings underscore the importance of ongoing research in uncovering the mysteries of our planet’s past. Beyond academic interest, this research provides valuable lessons about resilience and adaptation, themes that resonate with many aspects of modern life, including lifestyle choices we make.
In cities like Dallas, where lifestyle influences can vary greatly, the principles of adaptation and versatility serve as metaphors for our own local existence. Understanding the unique characteristics and benefits of living in different environments—urban versus rural—can enlighten choices about community engagement or personal pursuits.
Embracing the Evolutionary Narrative
The evolutionary narrative not only captures the essence of our biological history but also invites us to reflect on our place within the broader tapestry of life. As we continue to uncover more about our origins through fossils, we gain understanding and appreciation for the ongoing story of life on Earth.
This continues to reveal the interconnectedness of species and how understanding these connections can teach us vital lessons about adaptation in our fast-changing world.
 Add Element
Add Element  Add Row
Add Row 


Write A Comment